Here we go again.
The familiar scene plays out as you hear your spouse’s voice rise in anger. They’re targeting you and criticizing you again for something you’ve done wrong. Why is it always my fault? I never see other couples fighting like this. You feel beaten down, exhausted, and maybe even a little ashamed.
But as your spouse’s criticism digs deeper, your tone subtly starts to shift. You raise your voice in response: “You think I’m the problem? It’s not like you’re helping!” You then launch into your own volley of criticisms, anger causing you to yell and berate your spouse, saying things you know you’ll later regret. In your rage, you might even break things or throw an object across the room.
As you unleash your anger, you notice a look of fear cross your spouse’s eyes. Suddenly you get hit with a wave of guilt. What am I doing? I shouldn’t be yelling. Why did I let my temper get out of hand? You start to backpedal, looking for ways to make your spouse feel better. You make promises to change, to be more loving and kind, to help out around the house more often, whatever it is to appease the situation.
And perhaps you succeed at this for a day or two, but eventually you feel taken advantage of once again. You see yourself trying to change, but your spouse hasn’t changed at all. As your annoyance rises, you decide to bring it up again, and your spouse reacts in anger.
And so the cycle begins again.
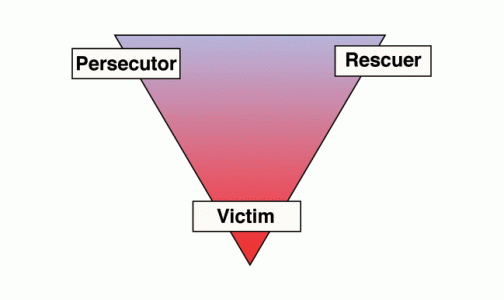
The Karpman Drama Triangle
Does this sound familiar to you? The scene above describes the power dynamics at play in the Karpman drama triangle. Stephen Karpman (https://www.karpmandramatriangle.com/) a psychiatrist specializing in transactional analysis, developed this model to describe the constantly shifting power dynamics in relationships. These dynamics are common in addictive relationships.
Image Source: https://www.lynneforrest.com/articles/2008/06/the-faces-of-victim/
We all play each of these three roles in our relationships, but you may tend to start your spiral around the triangle in one of the three types: victim, persecutor, or rescuer. Where you join the triangle stems from your experiences in your family-of-origin. You might even find yourself experiencing all three roles internally, as you use internal criticism to try to motivate yourself (persecutor), only to become exhausted and overwhelmed (victim) and attempt rescuing yourself from your pain through addiction or numbing behaviors (rescuer).
Taking on any one of these three roles provides a distraction from your own issues that need to be addressed or the true problem. While these patterns are learned in childhood from watching others interact and communicate, they may no longer be serving you. Eventually, all roles lead back to the victim, which adds to feelings of powerlessness to change.
Let’s learn about how these three interact.
The Victim
The victim is the “one down” position in the triangle. In the victim role, you feel like a child or overly needy. You might feel targeted or blamed with accompanying feelings of shame. This shame often originates in past trauma. The victim has unrealistic expectations of others and therefore is often disappointed when others don’t come through.
Often these expectations have to do with nurture or care, which victims feel incapable of providing for themselves. In fact, the victim tends to feel unable to handle any stress or negative circumstances, as their shame-based low self-esteem and negative beliefs about themselves limit them from any agency to change. Their lives happen to them rather than due to any power of their own. However, they still feel resentful from always being “one-down” and incapable of helping themselves.
An important note: the victim role is NOT equated with being a true victim of harm or abuse. Many victims (or as I prefer to say, survivors) or trauma or abuse in childhood or adult years are empowered, responsible, and strong individuals who are taking ownership of their lives in mature and assertive ways. If you are a survivor of trauma, abuse, or a spouse’s addiction, you ought to be treated with compassion for your experience of trauma. You did not ask for the harm done to you, nor did you deserve it in any way. The word “victim” here is meant to represent a role that is played in a relational dynamic that serves a protective purpose but ultimately doesn’t allow you to live into your true, authentic self.
The Perpetrator
The perpetrator role, in contrast with the victim, feels and acts like a teenager. They act out to deal with their discomfort or pain and protect themselves from the world, which they have learned is harmful and dangerous. Experiencing abuse in family-of-origin can often lead to learning to bottle up anger in a way that comes out int he perpetrator role later. Their behaviors are tied to feelings of shame, worthlessness, and fear.
This role is constantly defensive and has to be right, living in survival mode and lashing out at others. Their defensiveness is a way of regaining power when they’ve been victimized or harmed, as they fear being powerless in situations like they experienced in childhood. Viewing themselves as the true victim, the perpetrator’s behaviors are motivated by a desire to have the other person feel their pain. They often view the individual in the victim role with contempt and believe that their retaliation toward the victim Is simply giving the other person what they deserve. Perpetrators may think, “I have to hurt them before they hurt me.”
In a relationship with addiction present, this is often the addict. They are caught up in denial of their behaviors and have a difficult time admitting to their own experience of harming others. This can be understood in light of the shame they feel: to admit that they are the perpetrator would be devastating to their need to be strong in the face of feelings of powerlessness.
The Rescuer
The rescuer is the “one up” position, typically characterized by feeling like a parent and superior to the two other roles. Another way of categorizing this role is as a caretaker, which is often where many rescuers find their identity. In addictive dynamics, this person is the enabler of the addict. They often don’t like conflict or confrontation, and would rather smooth things over.
The rescuer’s “help” is meant not to truly benefit the other person, but instead to assuage their own anxiety and allow them to feel valued. They believe that if they don’t help, everything will fall apart. The rescuer can related to the victim in a codependent manner as they try to fix or save others. In fact, they need to have someone to save, and can assume others can’t handle something and then take over.
Rescuers don’t have needs – or at least, they deny that they do. Since they are the one who helps everyone else and their value comes from this identity, they either don’t admit to their own needs or don’t see them as important. Similar to the other roles, this tendency begins in childhood. Eventually, however, the endless helping turns into feelings of resentment and bitterness, as they expect affirmation and appreciation for all they’ve done for others. Yet they believe that if they are needed, they are loved, and are fearful of being abandoned if they stop helping.
In the next part, we’ll go into more depth about how to escape from the drama triangle through taking responsibility for yourself and your choices and setting boundaries. For now, notice these patterns in your interactions with others. How did your family interact with one another while you were growing up? Where have you seen examples of these dynamics play out in your life or in the lives of others?